The production of high-temperature textiles, in the last 40 to 50 years, has evolved significantly. Today, there is a wide range of options available on the market composed of human-made fibers that are very safe as compared to traditional ingredients used previously. Modern options include fibreglass, ceramic fibre, granite, clay, basalt, iron, stainless-steel or their unique combinations. These ingredients are of different weights, masses, densities, and yields, and these are all rendered into wool, cord, cloth, pipe, tube, and felt in specific requirements and coatings.
The cloths can be coated with PTFE fabrics, vermiculite, graphite, aluminum foil, acrylic, silicone and neoprene.
However prior to this, asbestos used to be the core ingredients for making high temperature fabrics worldwide for fireproofing, welding blankets and heat-insulation applications. Asbestos has many advantageous and unique properties and as it occurs naturally, it became an almost universal material but health concerns have rendered it almost completely obsolete these days.
New techniques are always being formulated and perfected to come up with a whole new range of modern insulation products. These modern insulation products have the ability to withstand any fluctuations in temperature.
Many refractory fabrics can easily be transformed into custom seals and speciality insulation. Applications include engine exhaust systems and industrial processing equipment.
Based on the specifications you require, high-temperature fabrics can be tailored to provide excellent resistance to abrasion, chemicals, contaminants, wind, noise, and vibration.
With modern water jet cutting and sewing capabilities, any leading manufacturer can turn felt, blankets, and fabrics into seals, expansion joints and insulation solutions. These cloths can be sewn with sewing threads of fiberglass yarns or kevlar. A professional production team can also manufacture different laminate types of materials to create thermal-acoustic insulation.
These cloths, such as glass fibre cloth, silica fibre, acrylic coated textiles, and laminated textiles, have a range of useful applications in commercial and residential environments. Let’s take a look.
Background on High-Temperature Fabrics
Throughout recent decades, high-temperature fabrics have seen a lot of innovation. Since asbestos health concerns have been uncovered, the thermal insulation industry has had to find alternatives to satisfy the growing demand for heat resistant fabrics.
Currently, heat resistant fabrics are made primarily of synthetic fibers, which surpass the efficiency that could be expected previously. These heat resistant fabrics come in a variety of sizes, but common forms involve boards, rope and tubing.
These are manufactured in a number of different ways, but are also designed in a variety of configurations in terms of thickness and width. Let us see how these fabrics are put to use.
Commercial Applications
High-temperature fiber insulation systems have become invaluable in most sectors around the globe. There are just some of the examples of commercial applications.
-
Military defence applications
-
Industrial insulation
-
Hydraulic applications
-
PPE (Personal Protection Equipment):
-
Industry and building sector
-
Paramedic and firefighting sector
-
Automotive industry
-
Aerospace
-
Metal industry
-
-
Clothing industry
Insulation in Military Applications
Flexible removable and powerful insulation blankets have been in use since World War 2. These have mainly been used for hot insulating pipes, engine sections, and exhaust sections on the military, coast guard ships.
During the 1970s, the Organization of the Petroleum Exporting Countries (OPEC) agreed to export oil out to the Continental United States. Following this, the industry sector in the United States planned their use of removable and reusable insulation.
During that period, the majority of commercial plants did not pay much attention to the pipes and internal machinery as long as the activity control or product quality was not in imminent danger. Currently, non-insulated machinery requiring high forms of maintenance running at 150°C / 299°F will produce a payback rounding up about one year’s worth.
This turns into sixteen to eighteen weeks at temperatures above 260°C / 499°F, or if enclosed with lightweight removable or reusable insulation. Modern fabrics and manufacturing methods allow lightweight removable blankets easy recycling. They can be recycled several times in processes with temperatures up to 760 °C / 1,399 °F without having vibrations that would typically jiggle apart any other type of insulation.
Thermal Insulation
The modern-day offers amazing fabric options at high temperatures that can easily manage any level of alkalinity in high-temperature processes without vibrating or shaking.
There are also improved versions of high-temp textile options for the creation of blankets for completely sound-proof. Flexible disposable or reusable fabric sheets are just a few of the high-temperature fiber applications.
Insulation of Hot Wires and Hydraulic Hoses
High-temperature braided tubing is composed of high-quality amorphous silica, carbon, or a combination of several other similar elements.
These knitted or braided materials can easily offer superior insulating properties for high-temperature and high-voltage wires and air-filled tubes.
Insulated wire, pipes, and tubes are usually enclosed inside machinery and are vital to the system's successful operation. If the device is to be made invulnerable against fire or insulated from raised temperatures, textiles with superior insulation are used to take care of that.
Personal Protection and Other Uses
Industry and Building Sector
High-temperature woven textiles are used in the industry and building sectors. These woven textiles are used in the form of high-heat-resistant curtains and welding blankets to shield and protect the operators and machinery from sparks or any other form of heat that might start a fire.
Factories may mark off certain regions of the environment as "Dangerous" during repair shutdowns or turnarounds. Subsequently, these fabrics are used as thermal barriers for the protection of the worker and other parties involved, including the equipment.
In the case of a grease fire, the majority of commercial kitchens utilize modern fire-resistant blankets to extinguish the flames, as adding water would only accelerate the fire.
In the event of a fire, many cinemas and other places use high-heat fabrics for protective measures. Recent developments with non-flammable curtains have led to the use of a material with PU coating, which allows light to pass through whilst still offering protection from smoke.
Paramedic and Firefighting Industry
In hot climates and conditions, high-heat resistant wool apparel is worn by our paramedics and firefighters. Man-made specialized fibers and glass fibre mixes are now leading the public sectors.
Innovative ways are constantly sought to help protect firefighters from the wildfires that are occurring around the globe.
Fabrics such as cotton, glass fibre, silica, carbon and felt are used individually to create boots, aprons and other personal heat protection attire for employees.
The Automotive Industry
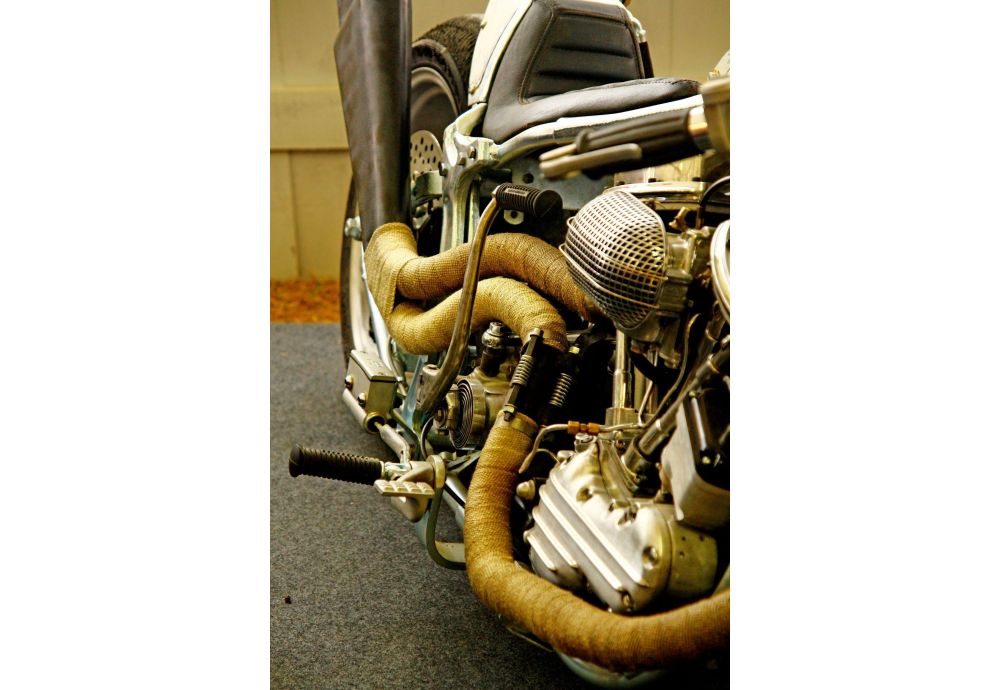
In the majority of vehicles, the car manufacturer takes advantage of the insulating and heat resistant textiles for fuel sections and exhausts.
The turbochargers and exhaust sections will reach 760°C /1400°F in higher power performance motors. Therefore, the separation of engine and commercial vehicle exhaust systems such as eighteen-wheelers, commercial tractors and construction machinery (cranes, etc.), is becoming increasingly necessary.
The modern race cars make exclusive use of fabrics with superior insulation as a comfortable and robust way to keep drivers relaxed, safe, and secure while they are on the race track.
The Aerospace Industry
The aerospace industry utilizes fabrics that withstand temperatures that are too high. Aircrafts take advantage of insulating blankets to keep everything safe and well-protected inside the cargo hold. For the creation of the compound resources for the aircraft and airliners, powerful carbon fiber fabric is used.
Many pressurized aircrafts utilize engine hot bleed air for air conditioning, ventilation, and controlling other functions. Heat resistant fabrics offer high forms of insulation and security in aircraft bleed air systems isolation along with bleed and disconnected ducting, hoses, plumbing, engine sections, and exhausts.
The Metal Industry
For a wide range of useful processes, the metal manufacturers are using textiles with high-temperature insulation.
High-heat textiles are rendered into insulating mats to protect steel and foundry workers from the excessive heat of the construction of liquid metals and heat-sensitive appliances. Often, such fabrics are used in the heat treatments and annealing phase to help uphold steady, regulated cooling.
The Clothing Industry
High-temperature textiles are used in manufacture where workers need to wear clothing with heat shielding properties. Such textiles, whether used for boots, aprons or full uniforms, dramatically reduce flammability and provide outstanding high temperature protection. The common use of these woven fabrics has been in motorsport, where racing car drivers and even pit crews are required to wear thermal shielding suits.
Hot Piping
Warm pipes are part and parcel of production, whether it's construction, chemical processing, or even shipping. High-temperature textiles are used to cover pipes that can pass their heat to neighbouring machinery, causing damage to them, or affecting certain operations that proceed. However, with emphasis on safety at the workplace, thermally resistant covers, and the like we're introduced to prevent accidental injuries to employees and improve working conditions.
Barricades
High-temperature textiles are used to protect staff from sparks and spatter in the shape of factory curtains and other types of barricades. These also secure workers working next to high-thermal performance machines such as furnaces and motor machinery.
Glass Fibre Felts and Blankets

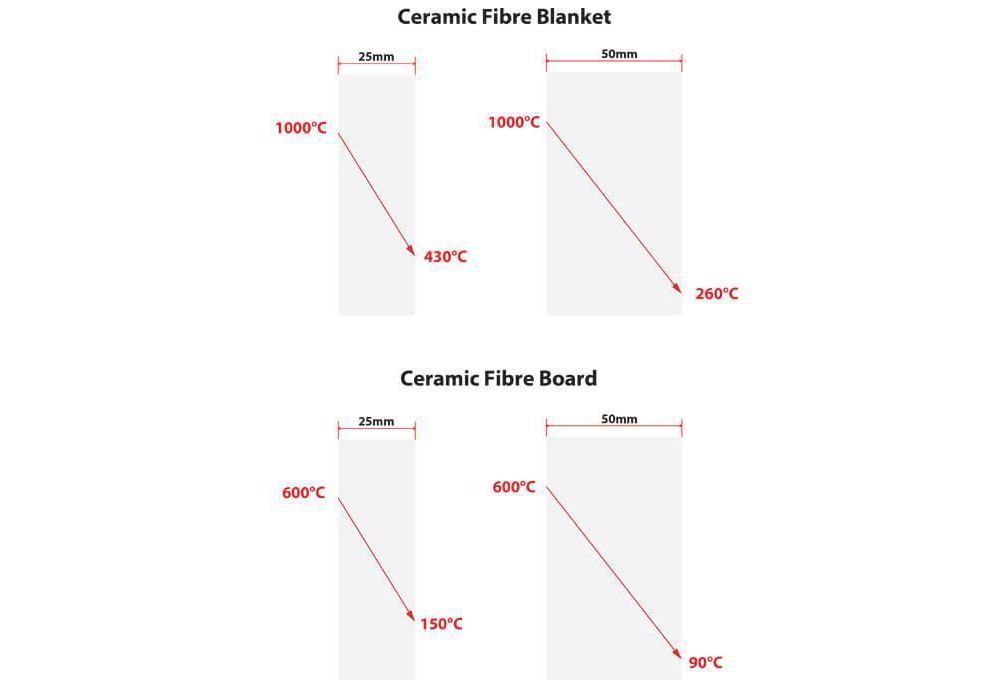
On the market there are two types of high-temperature felt and mats that are incombustible and asbestos-free to customize. The needled e-glass materials can withstand temperatures as high as 650°C / 1200°F.
It is often used in machinery because E-glass avoids vibrations. Silica textiles aid in providing sufficient insulation for the equipment thermally but can withstand the maximum continuous operating temperature as high as 980°C / 1800°F. It is also a good choice for engine exhaust systems, due to its high-temperature applications.
Silica-fiberglass composite materials incorporate the fiberglass cost-effectiveness with the silica fiber material properties. Uses provide thermal insulation and stress relief pads for processing equipment and engine exhaust systems.
Since it is long-lasting, it can help applications where disposable or reusable textiles are required. You can add straps and make your custom-made products simple to install and remove.
Treated Fabrics
The fabrics can also be converted at high temperatures. The silicone-coated fiberglass fabrics are a good choice for insulation jacketing. Such fabrics have the abrasion resistance and waterproof sealing in addition to the heat resistance. PTFE-coated fiberglass fabrics are used for chemical resistance. PTFE is a plastic fluoropolymer which is chemically inert to most acids and bases.
Heat treated materials also include silica, fiberglass foil, and stainless knitted mat. Constructed from high-purity, non-breathing silica yarns, silica fabrics can have a valuable tensile strength of 980°C / 1800°F and a melting point of 1650°C / 3000°F.
Fiberglass aluminized materials provide an impressive vapor barrier against moisture and other substances. These make of silver foils and films laminated to materials crafted from fiberglass. Stainless knitted covers comprise small, yet solid, stainless steel wire lines.
Graphite Gaskets
Unlike other types of gasket products, the mechanical properties of high temperature fabricated graphite rise with the temperature. Graphite can be sandwiched with other gasket materials (such as foils) in multi-layer components to create custom thermal seals and insulating solutions. Graphite is also flexible and has high durability which are suitable characteristics for demanding applications without fillers or binders, which may limit sealing performance.
Heat Blankets
Ventilation covers consist of silicone-coated, glass fibre sheets, durable fabrics, and Kevlar / Aramid or fiberglass cord.
Many products use press studs, while others utilize Velcro for a remedy that is completely non-metallic and will not rust. The built-in fasteners we provide are easy to attach and securely hold in place, but also convenient to detach when maintenance of the engine is required.
Steam Applications
Power Plant Industry
Power plants utilize textiles with high temperatures exclusively. The majority of the condensate devices use insulation mats for the tubes, fittings, and appliances.
The steam-powered machinery makes use of the modern and tailored heat resistant mat in the turbine area to prevent the condensate from developing. Generators, exhaust systems and natural-gas-powered systems also use these textiles for their insulation properties.
The Food Sector
High-temperature cloths are used by the food processing sector to insulate ovens and other machinery, such as chimneys.
PTFE fabrics are used to produce conveyor belts that are used to create processed food. Special impregnated PTFE or Teflon, high-heat textiles are also heavily utilized in the processing industry as a chemical splash shield to take care of the products.
The Pulp and Paper Industry
The pulp and paper industry is using textiles that are heat proof in their processes. Due to their radiant heat protection and aggressive chemical resistance properties, PTFE impregnated fiberglass fabrics are often utilized as covers.
Big boiler houses produce a lot of steam for the drying process throughout the papermaking process and offer other perks during the process. Removable blankets are used here to prevent the steam from hurting anyone during the process.
High-Temperature Insulation Textiles
Fibre insulation has served to separate the majority of the firmest and most complex devices men have built for themselves.
The goal for the coming years is to continue improving high-heat fibres so that they withstand high temperatures, are resistant to chemicals and are safe, whether it is silk fiber, fiberglass yarns, satin weave, ceramic fabrics etc.
What Do We Have to Say?
High-temperature textiles, such as glass fibre cloth, ceramic fabrics reinforced with wire, coated fabrics, and laminated products, are in high demand nowadays. These products offer a great level of resistance against heat, temperature fluctuations and electrical outages.
High temperature fabricated cloths are used in the manufacturing of flexible insulation covers, pipelining, generator sheets, fittings and flange coverings, welding curtains and exhaust pipe coverings for motors.
High-Temp Fabrics are suitable for a range from 150°C / 300°F to 1260°C / 2300°F. Many are made with heatproof yarns, and different additives and coatings can be added.
Many industries utilise these fabrics for their daily, routine activities to protect their machinery and personnel from heat-related accidents. Aerospace, defence, medical and healthcare, mobile equipment, and stainless steel and food industries use these fabrics on a daily basis to fight against sudden outages of electrical equipment and heat surcharges.
These fabrics can also be used for industries that use a excessive levels of heat to formulate different products on a daily basis. Heat resistant fabricated cloths can keep the heat away, and protect the items inside. These are suitable for use in hot environments.